Page 203 - Kỷ yếu hội thảo khoa học lần thứ 12 - Công nghệ thông tin và Ứng dụng trong các lĩnh vực (CITA 2023)
P. 203
Cong Tung Dinh, Thu Huong Nguyen, Huyen Do Thi, Nam Anh Bui 187
total number of points classified in that class. The Recall value is the ratio of the
number of correctly identified points in a class to the total number of data points in
that class. The F1-score quantity is the harmonic average determined based on two
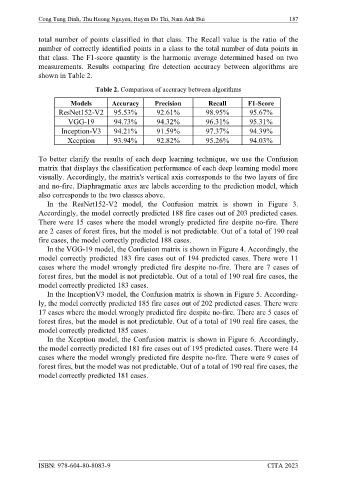
measurements. Results comparing fire detection accuracy between algorithms are
shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Comparison of accuracy between algorithms
Models Accuracy Precision Recall F1-Score
ResNet152-V2 95.53% 92.61% 98.95% 95.67%
VGG-19 94.73% 94.32% 96.31% 95.31%
Inception-V3 94.21% 91.59% 97.37% 94.39%
Xception 93.94% 92.82% 95.26% 94.03%
To better clarify the results of each deep learning technique, we use the Confusion
matrix that displays the classification performance of each deep learning model more
visually. Accordingly, the matrix's vertical axis corresponds to the two layers of fire
and no-fire. Diaphragmatic axes are labels according to the prediction model, which
also corresponds to the two classes above.
In the ResNet152-V2 model, the Confusion matrix is shown in Figure 3.
Accordingly, the model correctly predicted 188 fire cases out of 203 predicted cases.
There were 15 cases where the model wrongly predicted fire despite no-fire. There
are 2 cases of forest fires, but the model is not predictable. Out of a total of 190 real
fire cases, the model correctly predicted 188 cases.
In the VGG-19 model, the Confusion matrix is shown in Figure 4. Accordingly, the
model correctly predicted 183 fire cases out of 194 predicted cases. There were 11
cases where the model wrongly predicted fire despite no-fire. There are 7 cases of
forest fires, but the model is not predictable. Out of a total of 190 real fire cases, the
model correctly predicted 183 cases.
In the InceptionV3 model, the Confusion matrix is shown in Figure 5. According-
ly, the model correctly predicted 185 fire cases out of 202 predicted cases. There were
17 cases where the model wrongly predicted fire despite no-fire. There are 5 cases of
forest fires, but the model is not predictable. Out of a total of 190 real fire cases, the
model correctly predicted 185 cases.
In the Xception model, the Confusion matrix is shown in Figure 6. Accordingly,
the model correctly predicted 181 fire cases out of 195 predicted cases. There were 14
cases where the model wrongly predicted fire despite no-fire. There were 9 cases of
forest fires, but the model was not predictable. Out of a total of 190 real fire cases, the
model correctly predicted 181 cases.
ISBN: 978-604-80-8083-9 CITA 2023