Page 99 - Kỷ yếu hội thảo khoa học lần thứ 12 - Công nghệ thông tin và Ứng dụng trong các lĩnh vực (CITA 2023)
P. 99
Thanh Trung Nguyen, Hai Bang Truong 83
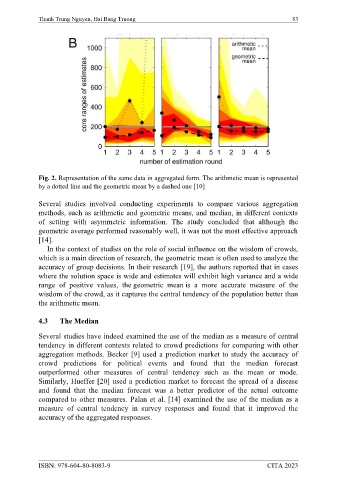
Fig. 2. Representation of the same data in aggregated form. The arithmetic mean is represented
by a dotted line and the geometric mean by a dashed one [10]
Several studies involved conducting experiments to compare various aggregation
methods, such as arithmetic and geometric means, and median, in different contexts
of setting with asymmetric information. The study concluded that although the
geometric average performed reasonably well, it was not the most effective approach
[14].
In the context of studies on the role of social influence on the wisdom of crowds,
which is a main direction of research, the geometric mean is often used to analyze the
accuracy of group decisions. In their research [19], the authors reported that in cases
where the solution space is wide and estimates will exhibit high variance and a wide
range of positive values, the geometric mean is a more accurate measure of the
wisdom of the crowd, as it captures the central tendency of the population better than
the arithmetic mean.
4.3 The Median
Several studies have indeed examined the use of the median as a measure of central
tendency in different contexts related to crowd predictions for comparing with other
aggregation methods. Becker [9] used a prediction market to study the accuracy of
crowd predictions for political events and found that the median forecast
outperformed other measures of central tendency such as the mean or mode.
Similarly, Hueffer [20] used a prediction market to forecast the spread of a disease
and found that the median forecast was a better predictor of the actual outcome
compared to other measures. Palan et al. [14] examined the use of the median as a
measure of central tendency in survey responses and found that it improved the
accuracy of the aggregated responses.
ISBN: 978-604-80-8083-9 CITA 2023